import geopandas as gp
import geodatasets
from plotnine import (
ggplot,
aes,
coord_fixed,
facet_wrap,
geom_map,
geom_text,
labs,
scale_fill_brewer,
scale_fill_continuous,
scale_x_continuous,
scale_y_continuous,
scale_size_continuous,
stage,
coord_cartesian,
element_line,
element_rect,
element_text,
theme_void,
theme,
)The Territories of Westeros
map
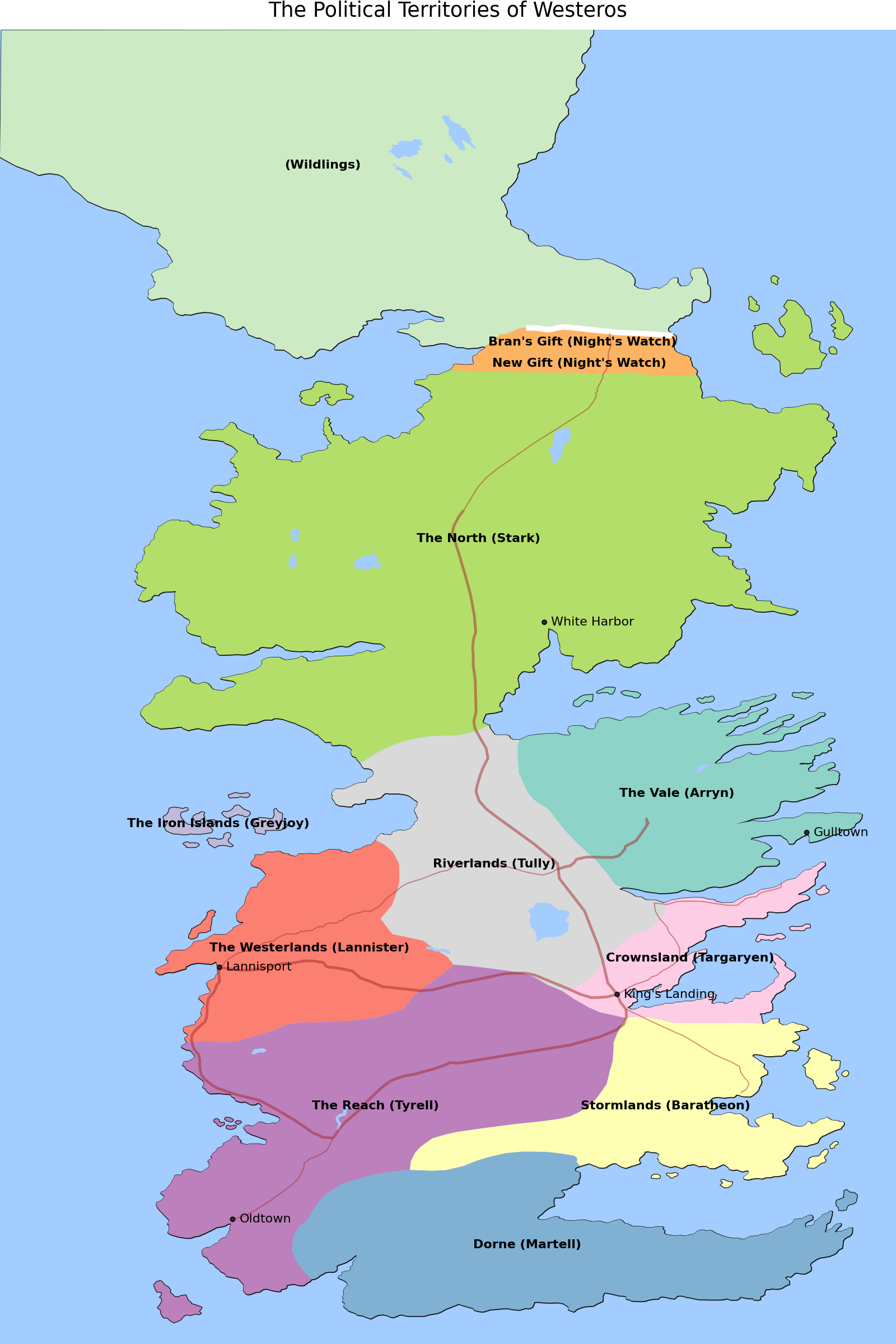
Layering different features on a Map
Read data and select features in Westeros only.
continents = gp.read_file("data/lands-of-ice-and-fire/continents.shp")
islands = gp.read_file("data/lands-of-ice-and-fire/islands.shp")
lakes = gp.read_file("data/lands-of-ice-and-fire/lakes.shp")
rivers = gp.read_file("data/lands-of-ice-and-fire/rivers.shp")
political = gp.read_file("data/lands-of-ice-and-fire/political.shp")
wall = gp.read_file("data/lands-of-ice-and-fire/wall.shp")
roads = gp.read_file("data/lands-of-ice-and-fire/roads.shp")
locations = gp.read_file("data/lands-of-ice-and-fire/locations.shp")
westeros = continents.query('name=="Westeros"')
islands = islands.query('continent=="Westeros" and name!="Summer Islands"')
lakes = lakes.query('continent=="Westeros"')
rivers = rivers.query('continent=="Westeros"')
roads = roads.query('continent=="Westeros"')
wg = westeros.geometry[0]
bool_idx = [wg.contains(g) for g in locations.geometry]
westeros_locations = locations[bool_idx]
cities = westeros_locations[westeros_locations["type"] == "City"].copy()Create map by placing the features in layers in an order that limits obstraction.
The GeoDataFrame.geometry.centroid property has the center coordinates of polygons, we use these to place the labels of the political regions.
# colors
water_color = "#a3ccff"
wall_color = "white"
road_color = "brown"
# Create label text by merging the territory name and
# the claimant to the territory
def fmt_labels(names, claimants):
labels = []
for name, claimant in zip(names, claimants):
if name:
labels.append("{} ({})".format(name, claimant))
else:
labels.append("({})".format(claimant))
return labels
def calculate_center(df):
"""
Calculate the centre of a geometry
This method first converts to a planar crs, gets the centroid
then converts back to the original crs. This gives a more
accurate
"""
original_crs = df.crs
planar_crs = "EPSG:3857"
return df["geometry"].to_crs(planar_crs).centroid.to_crs(original_crs)
political["center"] = calculate_center(political)
cities["center"] = calculate_center(cities)
(
ggplot()
+ geom_map(westeros, fill=None)
+ geom_map(islands, fill=None)
+ geom_map(political, aes(fill="ClaimedBy"), color=None, show_legend=False)
+ geom_map(wall, color=wall_color, size=2)
+ geom_map(lakes, fill=water_color, color=None)
+ geom_map(rivers, aes(size="size"), color=water_color, show_legend=False)
+ geom_map(roads, aes(size="size"), color=road_color, alpha=0.5, show_legend=False)
+ geom_map(cities, size=1)
+ geom_text(
political,
aes("center.x", "center.y", label="fmt_labels(name, ClaimedBy)"),
size=8,
fontweight="bold",
)
+ geom_text(
cities,
aes("center.x", "center.y", label="name"),
size=8,
ha="left",
nudge_x=0.20,
)
+ labs(title="The Political Territories of Westeros")
+ scale_fill_brewer(type="qual", palette=8)
+ scale_x_continuous(expand=(0, 0, 0, 1))
+ scale_y_continuous(expand=(0, 1, 0, 0))
+ scale_size_continuous(range=(0.4, 1))
+ coord_cartesian()
+ theme_void()
+ theme(figure_size=(8, 12), panel_background=element_rect(fill=water_color))
)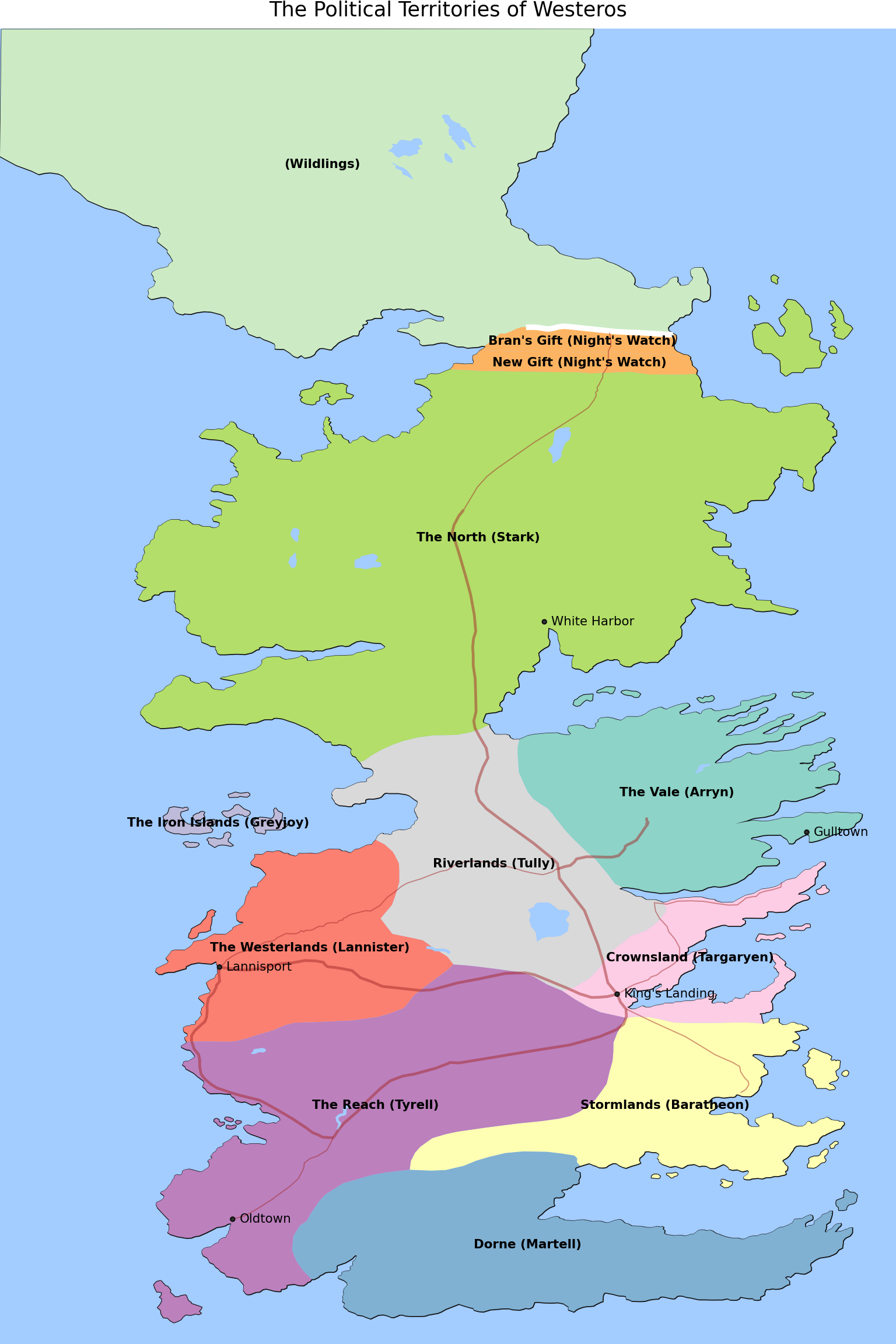
Credit: cadaei of the cartographersguild website forum.