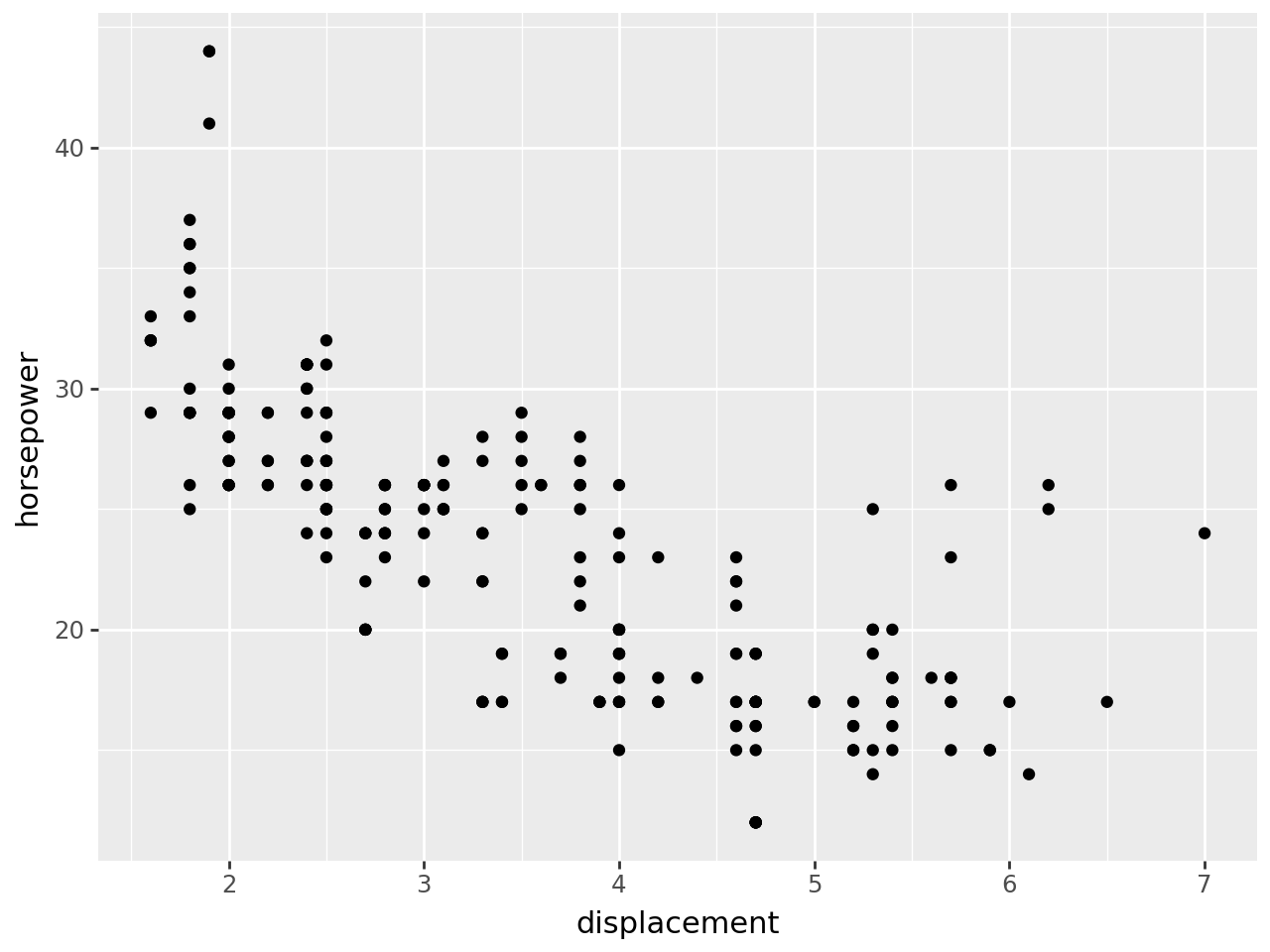
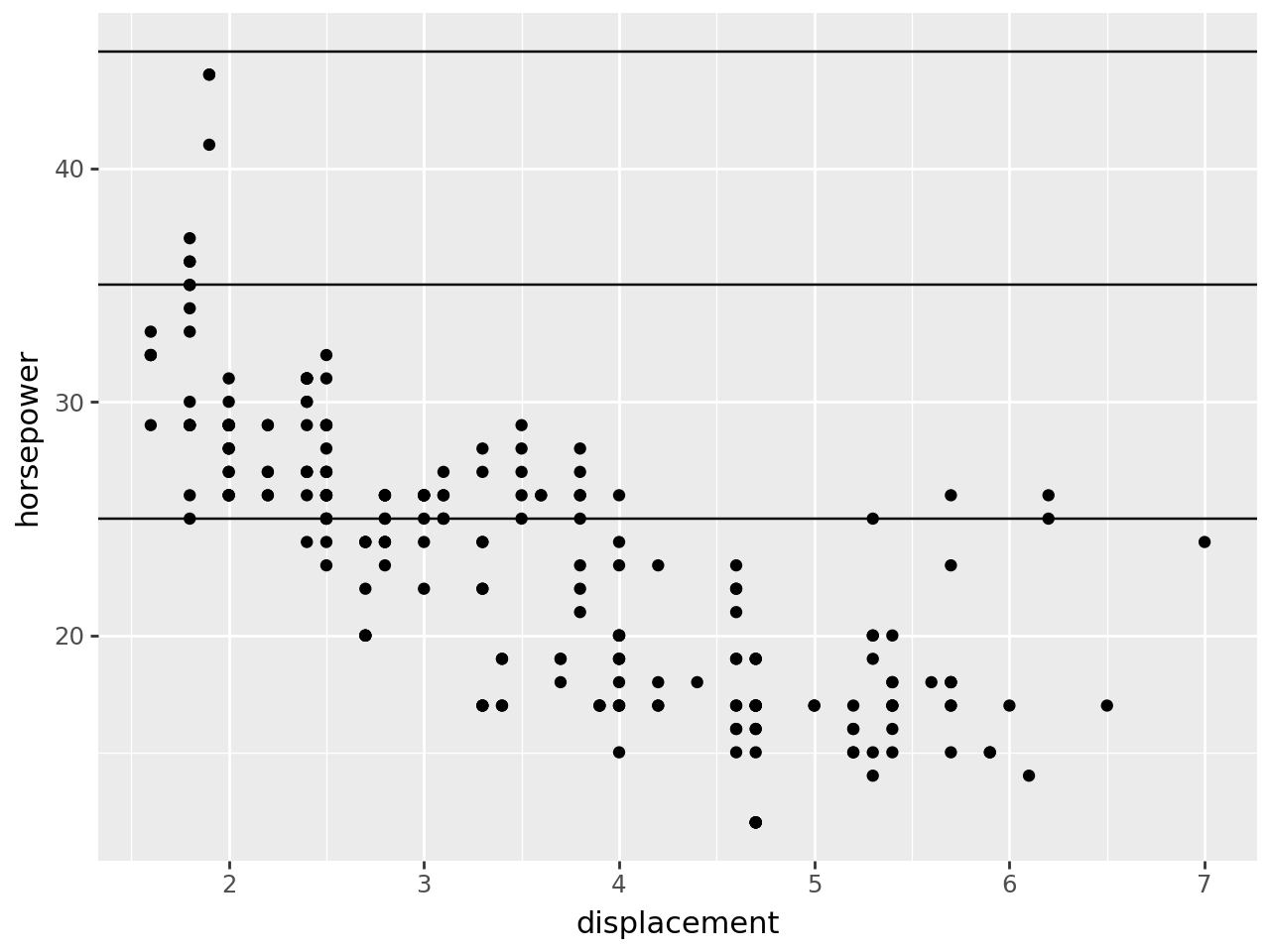
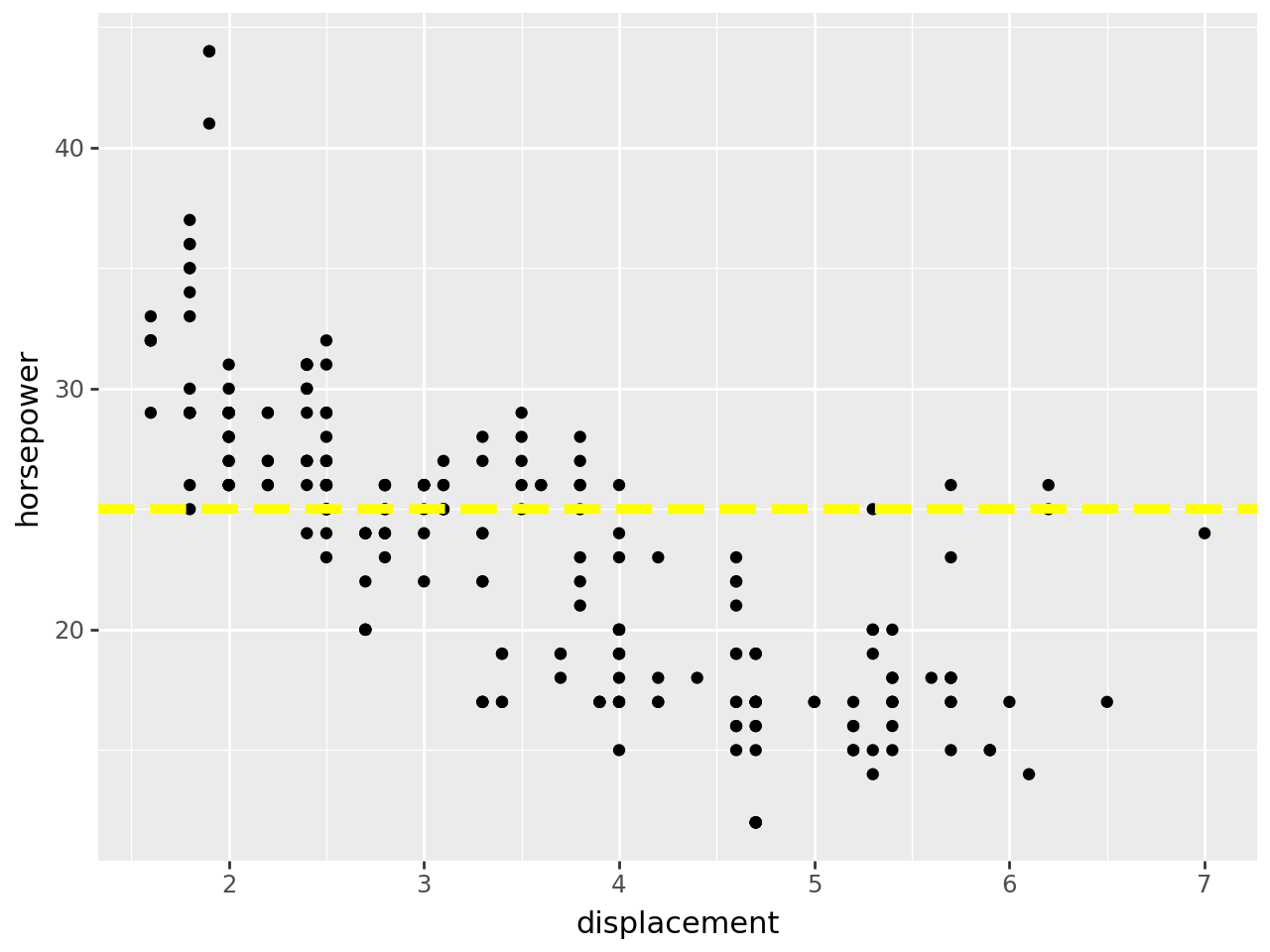
from plotnine import ggplot, aes, geom_point, geom_hline, facet_grid, labs
from plotnine.data import mpg
Horizontal line
geom_hline(
mapping=None,
data=None,
*,
stat="identity",
position="identity",
na_rm=False,
inherit_aes=False,
show_legend=None,
raster=False,
**kwargs
)Parameters
mapping : aes = None-
Aesthetic mappings created with aes. If specified and
inherit_aes=True, it is combined with the default mapping for the plot. You must supply mapping if there is no plot mapping.Aesthetic Default value yintercept alpha 1color 'black'group linetype 'solid'size 0.5The bold aesthetics are required.
data : DataFrame = None-
The data to be displayed in this layer. If
None, the data from from theggplot()call is used. If specified, it overrides the data from theggplot()call. stat : str | stat = "identity"-
The statistical transformation to use on the data for this layer. If it is a string, it must be the registered and known to Plotnine.
position : str | position = "identity"-
Position adjustment. If it is a string, it must be registered and known to Plotnine.
na_rm : bool = False-
If
False, removes missing values with a warning. IfTruesilently removes missing values. inherit_aes : bool = False-
If
False, overrides the default aesthetics. show_legend : bool | dict = None-
Whether this layer should be included in the legends.
Nonethe default, includes any aesthetics that are mapped. If abool,Falsenever includes andTruealways includes. Adictcan be used to exclude specific aesthetis of the layer from showing in the legend. e.gshow_legend={'color': False}, any other aesthetic are included by default. raster : bool = False-
If
True, draw onto this layer a raster (bitmap) object even ifthe final image is in vector format. **kwargs : Any-
Aesthetics or parameters used by the
stat.